| 2005 |

|
YEAR BOOK |
Radiological Protection Institute of Ireland
|
Upgrading the RPII's national radiation monitoring network
|
In an emergency, the rapid collection and interpretation of information is fundamental to any response. In the case of a national radiological/nuclear emergency, accurate data collection is essential for protection of the population. The information from an early warning system either through direct measurement or through global communication networks allows a decision to be made as to what countermeasures, if any, are necessary.
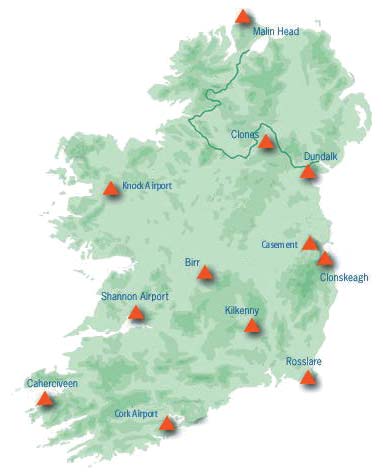
Gamma radiation dose rates are measured in units of nanosieverts per hour (nSv/h). The normal gamma dose rates vary with local geology and typically range from 50 to 120 nSv/h. Increases in the dose rate occasionally occur due to washout of radon decay products from the atmosphere. These increases are short-lived, lasting only an hour or two after rainfall has ended. The new monitoring network includes rainfall detection, which allows correction for this temporary increase in dose rate. Ambient gamma dose rate can be measured within the range 10 nanosieverts per hour up to 10 sieverts per hour using two duplicated low dose detectors and one high dose detector. Data reliability is enhanced by constant software comparison of the measurements from the duplicated detectors. An error message is generated if this comparison falls outside an allowable tolerance.
Forty mobile monitoring units operated by the Reserve Defence Force's Radiological Monitoring Teams are available to supplement the RPII's fixed stations. Civil Defence teams can also be called on to provide additional radiological monitoring in the event of wide scale contamination.
Contact: Radiological Protection Institute of Ireland,
3 Clonskeagh Square, Dublin 14;
Telephone: 01 2697766; Fax: 01 2697437;
Email: [email protected] ; Web: www.rpii.ie