| 2003 |

|
YEAR BOOK |
University of Limerick
|
Numerical analysis and computation at UL
|
At the University of Limerick, the focus is on the numerical solution of differential equations, in particular, singularly perturbation problems. Solutions of such problems typically have rapidly varying behaviour, such as boundary layers or shocks, in some parts of the problem domain and require specially designed algorithms if they are to be solved accurately. For example, they arise in fluid flow problems when a parameter known as the Reynolds number is large, for example when the fluid velocity is high.
Ireland has become an important centre for the numerical analysis of these problems, with research being carried out in TCD, DCU, NUIG and UCC as well as UL, with close collaboration between the various centres. In UL the numerical analysis group in the Department of Mathematics and Statistics comprises three faculty and two graduate students, and Professor G.I. Shishkin of the Russian Academy of Sciences has recently been appointed as an Adjunct Professor. The department has for the last two years hosted an annual workshop on the numerical solution of singular perturbation problems, which has had speakers from all the research centres in Ireland, as well as Russia, the USA and the Netherlands.
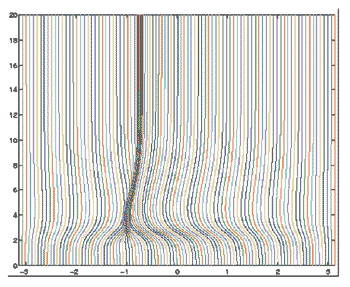
The particular methods of interest are Shishkin mesh methods, where computational meshes are fitted to the nature of the problem; moving mesh methods, where the computational mesh adapts automatically to the evolution of the problem solution (see Figure); and domain decomposition techniques, where the problem can be solved using different techniques on various subdomains, and the overall solution can be assembled using Schwarz iteration.
Contact: Dr Alan Hegarty; Tel: 061-202070; E-mail: [email protected]